The relationship between melt furnace and scrap metal recycling is fundamental in modern metallurgy. Scrap metal recycling is essential for reducing waste, conserving resources, and lowering energy consumption in metal production. Melt furnaces play a central role in this process by melting down scrap metals and transforming them into new, usable materials.
Role of Melt Furnaces in Scrap Metal Recycling
Scrap Metal Sorting and Pre-Treatment:
Scrap metals are generally categorized into two main types: ferrous metals (like steel and iron) and non-ferrous metals (like copper, aluminum, zinc, etc.). Proper sorting is critical to ensure the purity and quality of the metals after melting.
After sorting, scrap metals often undergo cleaning, removal of contaminants, and compression to reduce the emission of harmful gases and slag during melting and to improve melting efficiency.
Types of Melt Furnaces Used in Scrap Metal Recycling:
Induction Furnace: Commonly used for melting non-ferrous metals such as copper and aluminum. It heats metals using electromagnetic induction, which allows for fast melting, high efficiency, and precise temperature control.
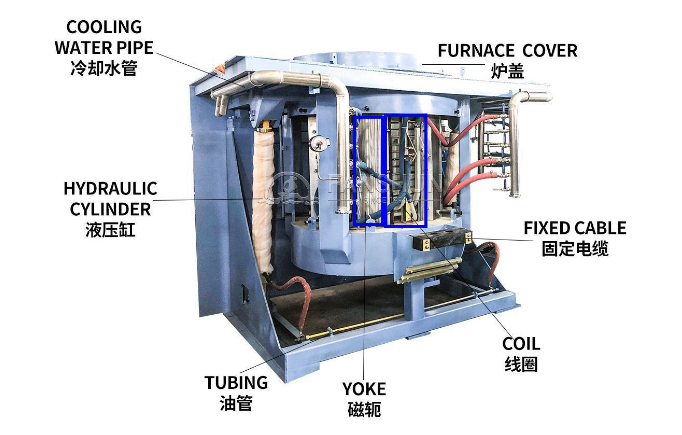
Electric Arc Furnace (EAF): Mainly used for large-scale recycling of steel scrap. The EAF melts scrap steel using electric arcs generated by electrodes, producing liquid steel that can be cast into various shapes.
Crucible Furnace: Suitable for small-scale melting and refining of scrap metals, particularly in foundries or laboratories. These melt furnaces use crucibles to hold and melt the metal, which can be heated using different methods such as gas, oil, or electricity.

Basic Oxygen Furnace (BOF): While primarily used for producing new steel, BOFs can also recycle scrap steel by blowing oxygen to oxidize impurities in the molten iron and scrap.
Melting Process of Scrap Metals:
After pre-treatment, scrap metals are fed into a melt furnace, where they are melted down using various heating methods (such as electric arc, induction, or flame). During melting, metals separate into layers or phases (such as molten metal and slag).
To improve the quality of molten metals, fluxes or reducing agents are often added to remove impurities and oxides. Fluxes help dissolve oxides and silicate slags, forming slag that is easy to remove.
Mixing and Homogenization:
During the melting process, melt furnace mixers or electromagnetic stirrers are often used to mix molten metals and additives to ensure uniform composition and prevent segregation.
Casting and Cooling:
Once the desired chemical composition and temperature are achieved, the molten metal is cast into molds to form new metal products (such as ingots, sheets, or bars). These new products can be used again in manufacturing industries, including construction, automotive, and electronics.
Advantages of Scrap Metal Recycling with Melt Furnaces
Resource and Energy Savings:
Recycling scrap metal consumes significantly less energy than extracting and processing new metals from ores. For instance, recycling aluminum uses only about 5%-10% of the energy required to produce new aluminum.
Environmental Benefits:
Recycling reduces the need for mining, thus minimizing environmental damage from ore extraction. It also reduces waste going to landfills and cuts down on greenhouse gas emissions and pollutants from primary metal production.
Cost Efficiency:
Recycled metals are generally cheaper to produce than new metals, providing significant cost savings to manufacturers. Additionally, companies benefit from lower waste disposal costs and potential revenue from selling recycled materials.
Supports a Circular Economy:
Scrap metal recycling is a key part of the circular economy, where resources are reused and recycled to minimize waste and optimize resource use.
Challenges and Solutions in Scrap Metal Recycling
Impurities in Scrap Metals: Scrap metals may contain contaminants like paint, plastic, or other materials that can release harmful gases when melted. Advanced pre-treatment technologies and furnace gas purification systems can effectively reduce pollutant emissions.
Control of Alloy Composition: The composition of recycled metals can be complex and inconsistent. Spectroscopic analysis and refining processes are employed to ensure that the metal composition meets the desired specifications.
Conclusion
Melt Furnaces play a crucial role in the recycling and reuse of scrap metals. Through the careful selection of processes and equipment, the efficiency of resource utilization can be maximized, and environmental impact can be minimized, leading to both economic and environmental benefits. Scrap metal recycling, supported by efficient melt furnaces, is not only a trend in industrial development but also a necessary choice for sustainability and environmental protection.
If you have any specific questions about melt furnaces or scrap metal recycling processes, feel free to ask!

